Loofahs, also known as luffas, are a popular choice for cleansing and exfoliating the skin during bathing.
Dermatologists, however, often advise against their use and suggest alternative tools.
The primary concerns relate to hygiene and the risk of skin infections due to bacterial growth on the loofahs.
What are loofahs made of?
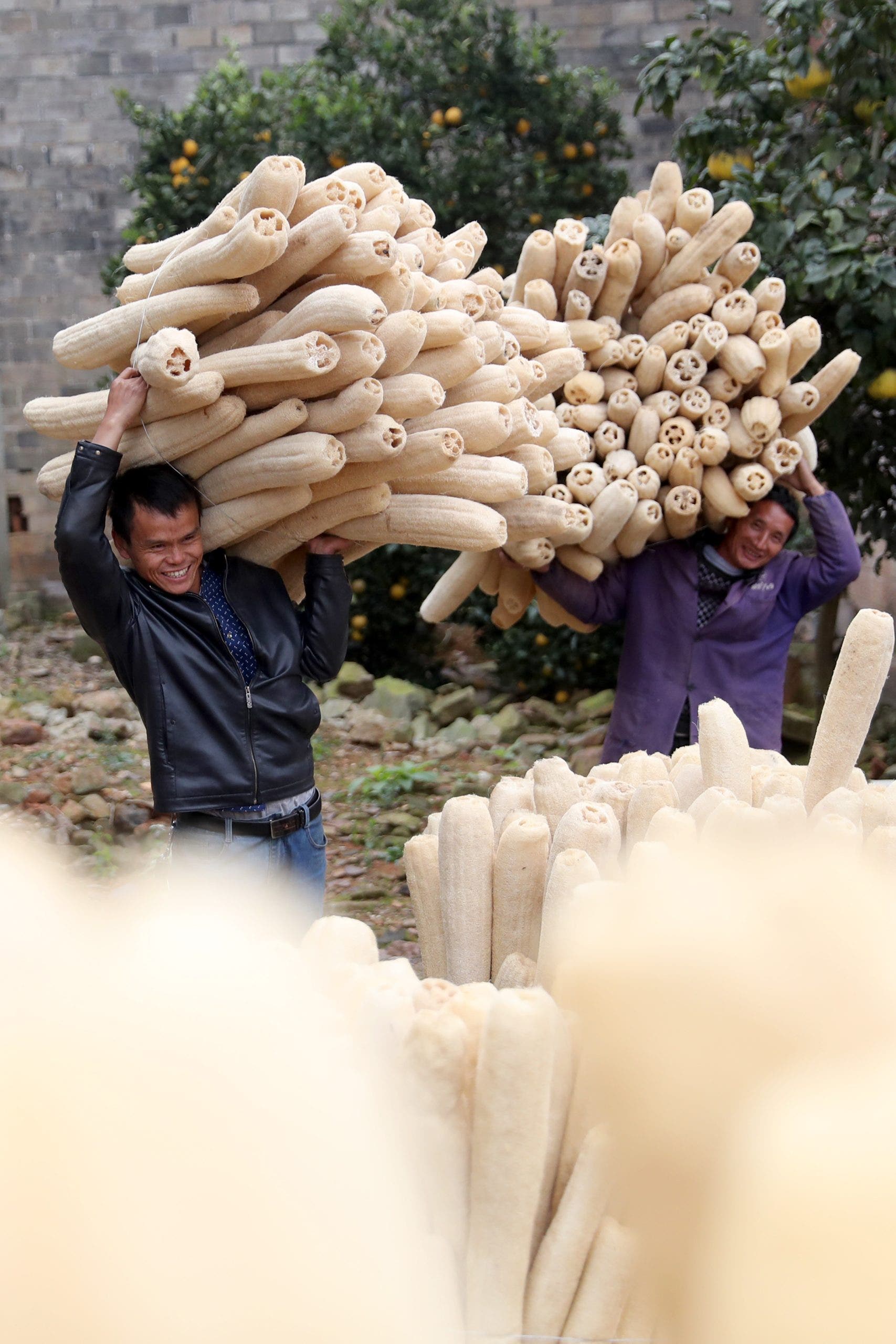
Loofahs, traditionally sourced from the fibrous interior of the luffa plant fruit, are used as a natural scrubbing sponge for cleansing and exfoliating the skin. This plant, part of the gourd family Cucurbitaceae that includes pumpkins and cucumbers, is peeled and dried to create the loofah sponge.
WOMAN’S VIRAL SPONGE HACK SAID TO BE MONEY-SAVING ALTERNATIVE TO DRYER SHEETS
Known for their exfoliating properties along with the ability to lather and cleanse, loofahs have been a long-standing bathroom staple.
Synthetic versions made from plastic or alternative materials are now commonly used.
Reasons to avoid using a loofah for bathing
Typically, loofahs are kept in the shower after use. The damp environment is a breeding ground for bacteria that clings to the loofah.
Loofahs can be dangerous because they are a “microbe reservoir,” according to MedicineNet.com. Since bathers use the loofah to scrub dead skin, the cells get wedged into the pores of the sponge, leading to bacterial growth.
“These act as a perfect environment for growth of bacteria, fungi and mold.”
The common types of bacteria that can grow on the loofah are Pseudomonas species and Enterobacteriales, says the National Library of Medicine.
They can also become the habitat of other bacteria such as E. coli.
ARE YOU WASHING YOUR BATH TOWELS ENOUGH? HERE’S WHAT EXPERTS HAVE TO SAY
Contaminated loofahs have even been linked to cases of Pseudomonas folliculitis, a skin infection caused by bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa that is usually developed from a public hot tub, pool or spa.
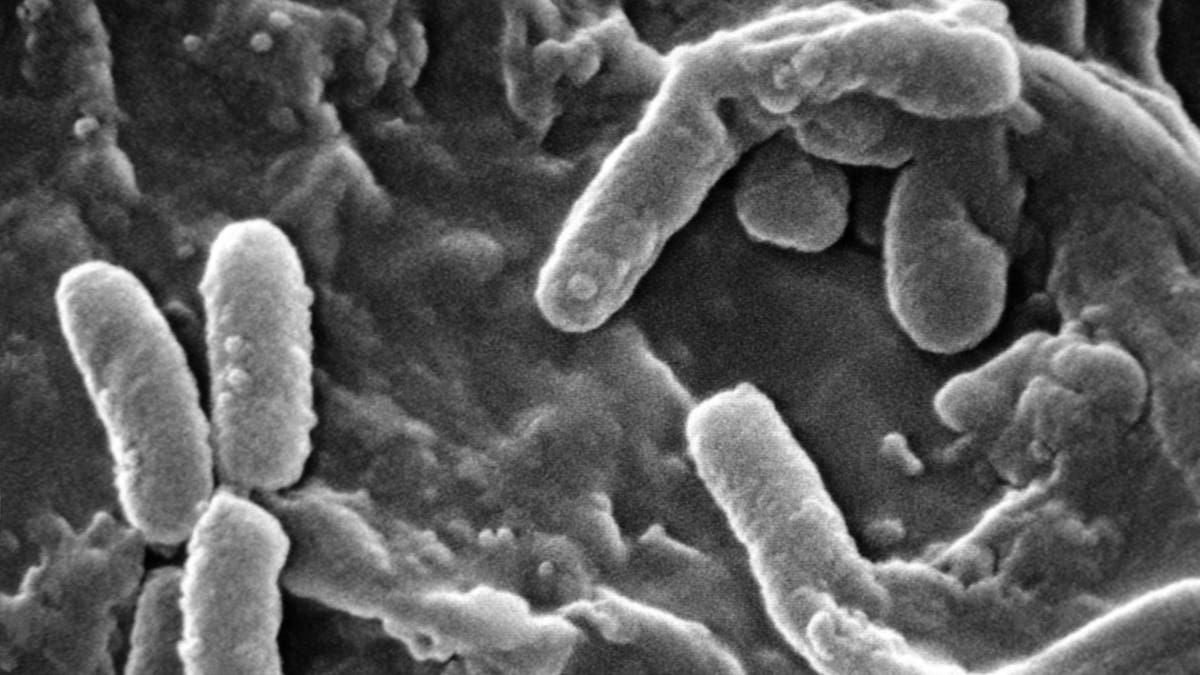
The bacteria that can thrive within the sponge, along with its potential to cause microtrauma due to abrasiveness, render loofahs an undesirable choice for many dermatologists.
They often suggest that if loofahs are used, they should be limited to once or twice a week and avoided entirely for several days post-shaving to prevent bacteria from entering through any small cuts on the skin.

How often should you replace your loofah?
It is generally recommended that you throw out a natural loofah after three to four weeks of use, which is also the recommendation of the Cleveland Clinic.
Plastic loofahs can last for two months. If the loofah shows signs of mildew or mold, however, it should be discarded immediately.
Alternatives to a loofah shower sponge
If you’re convinced that you should remove loofahs from your bathroom routine, it’s helpful to know the available alternatives.
For more Lifestyle articles, visit www.foxnews/lifestyle
Washcloths are a safer option since they can be washed frequently, reducing bacteria accumulation.

Silicone bath scrubbers are another alternative, although they require regular cleaning.
Sea sponges are a natural choice that come with enzymes to deter bacteria. They lack preservatives and dyes.
For those who prefer to continue using a loofah, it’s essential to clean it thoroughly and ensure it dries completely after each use.













